Omega-3 Fatty Acids: The Story of the Most Underestimated Nutrient of Modern Times
In a world where food is more abundant than ever, it’s paradoxical that most people suffer from a deficiency of one of the most important molecules for the brain and the heart — omega-3 fatty acids. For years, they were treated as a side note, a casual reminder that “it’s good to eat fish,” until science began to seriously examine what actually happens when these fats are missing.
Omega-3 deficiency doesn’t cause dramatic symptoms overnight. Instead, it acts as a silent, slow saboteur of health — influencing focus, mood, heart function, skin, hormones, and inflammatory processes. What makes them especially fascinating is that they work quietly, deeply, and gradually, yet over time they reshape the stability of the entire system.
If you want to understand how omega-3s work in synergy with other key nutrients, see the in-depth analysis
Vitamin D and Omega-3: Similarities, Differences, and When to Combine Them
What Are Omega-3s and Why Does the Body Need Them So Much?
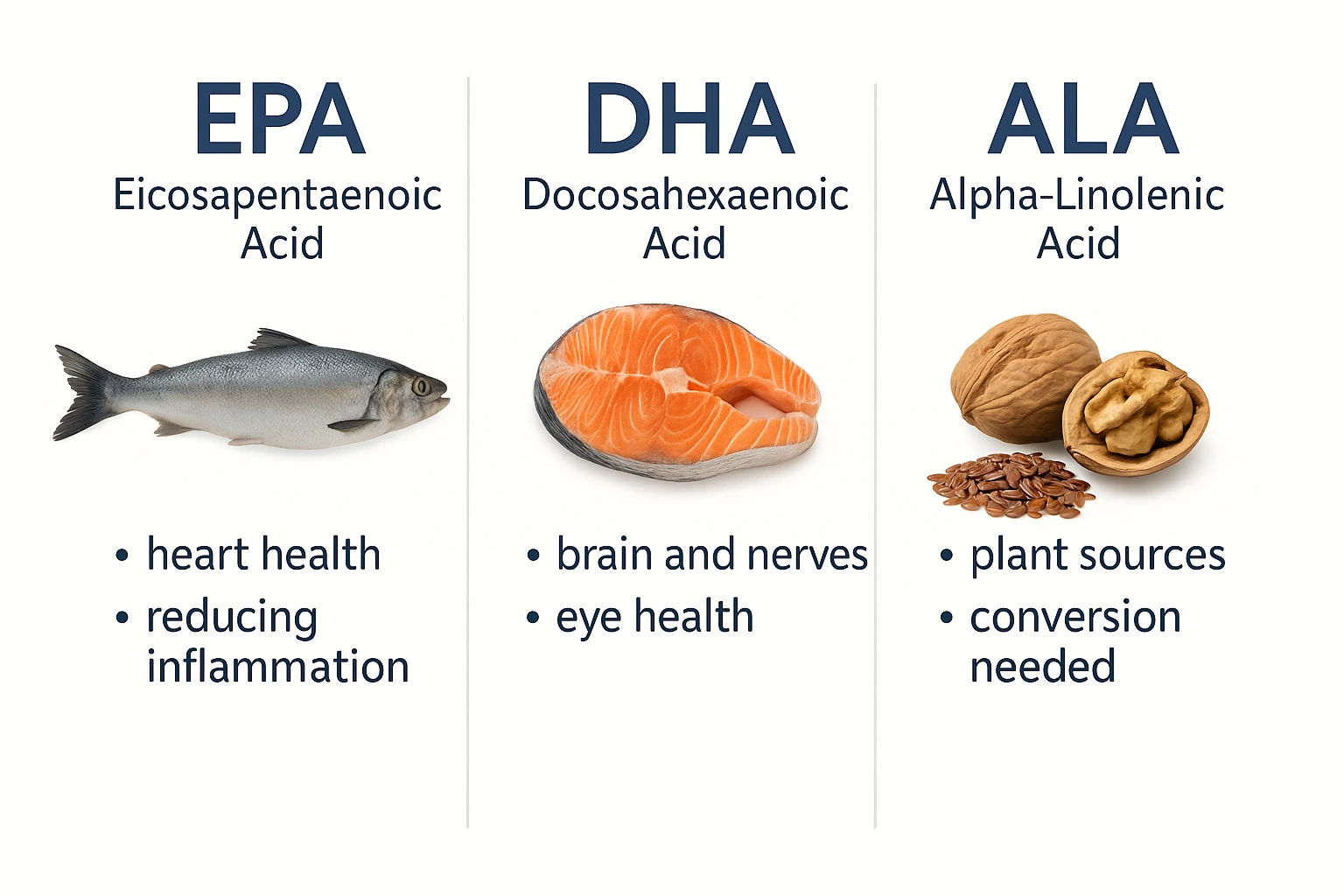
Omega-3s are essential fatty acids, meaning the body cannot produce them on its own. There are three key forms:
- DHA — the primary structural fat of the brain and retina
- EPA — a regulator of inflammation and emotional stability
- ALA — a plant-based form with very poor conversion to DHA and EPA
DHA forms the foundation of neuronal membranes, keeping the brain flexible and resilient, while EPA is the body’s main tool for calming inflammation. When they work together, the body functions more calmly, clearly, and robustly.
The Best Natural Sources of Omega-3: Where to Get the Most
While supplements can be useful, the best way to obtain omega-3s is through foods rich in EPA and DHA, as these forms are directly incorporated into the brain, eyes, and heart.
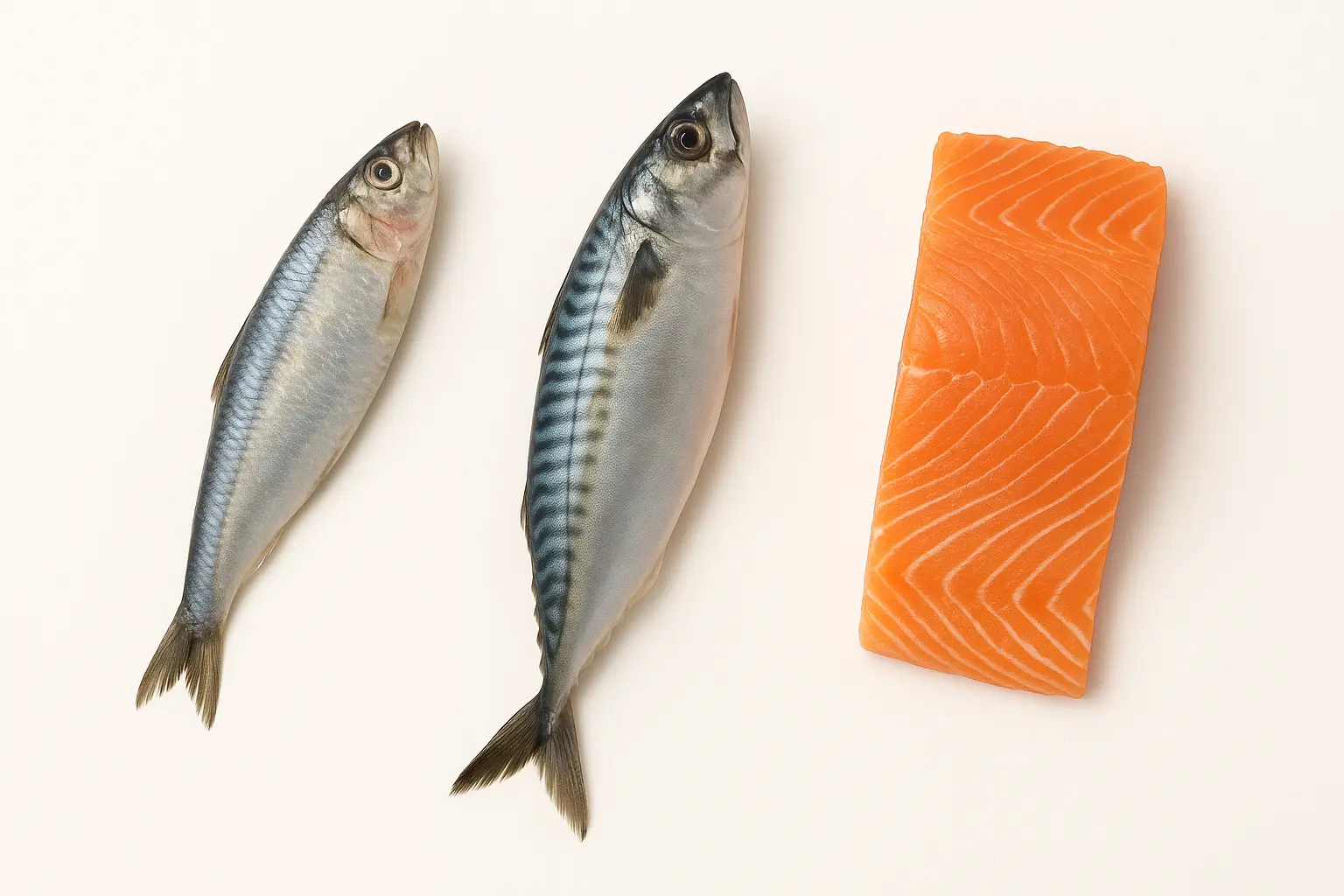
🐟 Fatty Fish — The Most Powerful Natural Source (EPA + DHA)
Fatty fish are unmatched because they contain the highest levels of active omega-3s and relatively low mercury.
EPA + DHA per 100 g:
- Mackerel — ~2500 mg
- Herring — ~2000 mg
- Sardines — 1500–1800 mg
- Anchovies — ~1500 mg
- Wild salmon — 1200–2000 mg
- Trout — ~900 mg
Practical recommendation:
2–3 servings of fatty fish per week cover most needs.

🌱 Plant Sources: Helpful, but Not Sufficient
Plants provide ALA, which the body converts to EPA/DHA at only 1–5% efficiency.
Top plant sources:
- flaxseeds
- chia seeds
- walnuts
- hemp seeds
They’re beneficial for general inflammation, but they do not replace DHA for the brain.
🧬 A Vegan Source Equal to Fish: Algal Oil
Algal oil is the only plant-based source that contains pure DHA + EPA.
It’s ideal for vegans and for pregnant women who avoid fish.
What Does Science Say? Three Key Research Stories
Omega-3 and Depression — The Role of EPA
A large meta-analysis found that EPA can significantly reduce symptoms of depression, particularly in individuals with chronic inflammation. Improvements were not sudden, but gradual, as inflammatory markers decreased and chemical signaling in the brain stabilized.
In practice, this means: fewer mood swings, clearer thinking, and greater emotional resilience.
DHA and the Brain — A Lifelong Nutrient
DHA makes up about 30% of the fat in the human brain, making it essential during pregnancy, childhood, and old age.
Studies show:
- infants born to mothers with low DHA have poorer neurological development
- older adults with higher DHA levels have a lower risk of dementia
- DHA improves working memory and processing speed
In other words — DHA is the architect of the brain.
Heart Health and Triglycerides — The Power of High Doses
Doses of 2–4 g of EPA + DHA per day can reduce triglycerides by up to 40%.
This is why pharmaceutical-grade omega-3s are used in metabolic syndrome therapy.
However, high doses also carry risk: an increased likelihood of atrial fibrillation — therefore only under medical supervision.
Omega-3 and Mental Clarity: Why They Affect Focus So Strongly
The neuronal membrane determines how quickly and accurately the brain processes information.
When DHA is sufficient, the membrane is flexible, stable, and highly conductive.
A similar stabilizing effect on the nervous system is seen with magnesium, which we cover in detail here:
Magnesium: How It Works, Who Really Needs It, and When It Can Be Dangerous.
When DHA is lacking, neuronal communication becomes slower and “noisier.”
Meanwhile, EPA reduces chemical brain noise, also known as neuroinflammation.
This is why many people notice:
- better focus
- less anxiety
- more stable mood
- easier decision-making

How to Choose a High-Quality Omega-3 Supplement
Fatty Acid Form — The Key Factor
- Triglyceride form → natural, stable, best absorption
- Ethyl ester form → cheaper, less bioavailable, more reflux
If the label doesn’t specify the form, it’s almost certainly ethyl ester.
EPA and DHA Content Matters More Than Total Oil Amount
Many products contain 1000 mg of oil per capsule but only 200 mg of EPA/DHA.
That’s too weak for a real effect.
Oil Freshness — The Most Important Safety Factor
Fish oil that smells “fishy” is oxidized.
Look for:
- IFOS certification
- low TOTOX values
- oil sourced from cold-water fish
My Research Notes: How I Personally Experienced Omega-3
Unlike many supplements I’ve tried, omega-3s produced a noticeable effect after a few weeks — not a sudden change, but a gentle system-wide alignment. Like straightening your posture and suddenly realizing your body moves more smoothly — except this time, it was happening in my head.
I noticed two subtle but clear signals:
- less mental noise
- a more stable emotional rhythm
My focus lasted longer — not as a burst of energy, but as steadiness, the ability to stay on one thought without constant distraction.
What fascinated me most was that omega-3s didn’t feel like they were “adding something,” but rather removing what was in the way: tension, reactive thinking, small energy blockages.
Not spectacular — but stable, quiet, and real.
Personalized Protocols: How to Use Omega-3 Based on Your Goal
1. Focus and Cognitive Work
- 600–1000 mg DHA
- 300–600 mg EPA
2. Inflammation and Joint Health
- 1000–1500 mg EPA
- 300–500 mg DHA
3. Pregnancy and Breastfeeding
- 300–600 mg DHA (algal oil is an excellent option)
4. Heart Health
- around 1000 mg EPA + DHA daily
(High doses — only with medical supervision.)
Side Effects and Precautions
Omega-3s are very safe, but they can:
- thin the blood
- cause reflux when taken on an empty stomach
- increase arrhythmia risk at high doses
If you are on anticoagulants or have cardiac arrhythmias, caution is advised.
FAQ — Short Answers
When do they start working?
After 4–12 weeks.
Can you take too much?
Yes — more than 3 g of EPA+DHA increases bleeding and arrhythmia risk.
Do they help with ADHD?
DHA shows promising results in children with low omega-3 status.
Can they be combined with vitamin D?
Yes — and it’s recommended.
Conclusion
Omega-3s are not a trend — they are the molecular infrastructure of health.
They build the brain. Protect the heart. Regulate inflammation. Stabilize mood.
They don’t create dramatic overnight changes, but they deliver what matters most:
long-term stability, mental clarity, and resilience.
📚 Recommended Resources
Examine.com – Omega-3
Harvard Nutrition – Omega-3 Overview
IFOS Database
Meta-analysis on Depression and EPA
DHA and Cognitive Health
🔗 Related Articles on Reviewetics
Vitamin D and Omega-3: Similarities, Differences, and When to Combine Them
Magnesium: How It Works, Who Really Needs It, and When It Can Be Dangerous
Ashwagandha: Everything You Need to Know About This Powerful Adaptogen
This article is for informational and educational purposes only. It is not medical advice and does not replace professional diagnosis or treatment. If you have a medical condition or take medication, consult a healthcare professional before using dietary supplements.


